-
EURIDIS/ADONIS study design1
- Double-blind, randomized, multicenter studies evaluating efficacy and safety of MULTAQ® in maintaining sinus rhythm in 1237 patients with nonpermanent AFib/AFL
- Patients with at least 1 episode of AFib/AFL observed on an ECG 3 months prior to study enrollment and in sinus rhythm for at least 1 hour prior to randomization were assigned to 400 mg MULTAQ (n=828) twice daily or placebo (n=409) for 12 months
- Primary endpoint: First documented recurrence of AFib/AFL, defined as an episode lasting for ≥10 minutes, and confirmed by 2 consecutive ECGs taken 10 minutes apart on ECG or transtelephonic monitoring (TTEM), within the 12-month period
Common CV comorbidities in patients in the
MULTAQ EURIDIS/ADONIS trials
TYPICAL AFIB PATIENTS
(N=1237)1,2
57% Hypertension
41% Structural heart disease
22% Coronary artery disease
17% CHF (NYHA Class I/II)
MULTAQ is contraindicated in patients with NYHA Class IV heart failure, symptomatic heart failure with recent decompensation required hospitalization, and permanent AF.2Common cardiovascular therapies treating
patients in the MULTAQ and placebo arms1TYPICAL AFIB PATIENTS
(N=1237)1,2
70% Oral anticoagulant
56% Beta-blocker excluding sotalol
39% ACE inhibitor
32% Statin
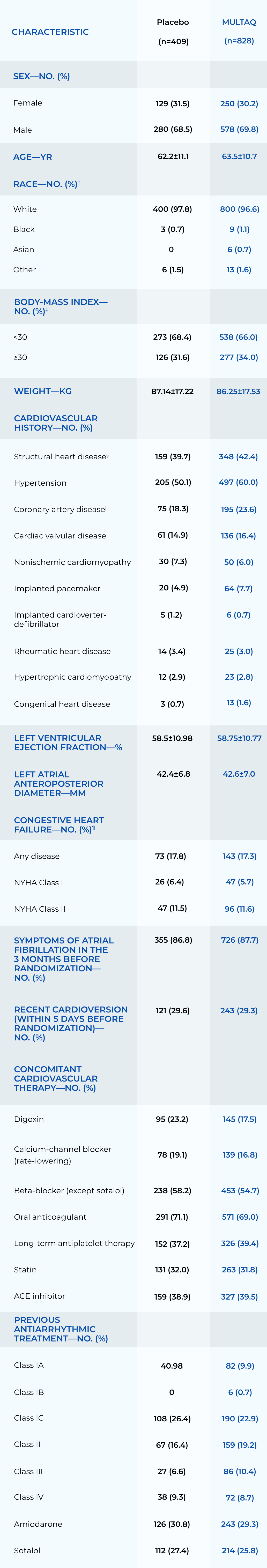
18% Calcium channel blockerBaseline characteristics of the study patient1,*

*Plus–minus values are means ±SD.
†Race was determined by the investigators on the basis of hospital records.
‡The body-mass index was calculated as the weight in kilograms divided by the square of the height in meters.
§In the European trial, data were missing for 6 subjects in the placebo group and 6 in the MULTAQ group; in the non-European trial, data were missing for 4 subjects in the placebo group and 7 in the MULTAQ group.
||The diagnosis of coronary artery disease was made on the basis of the clinical history and the results of investigational tests.
¶The diagnosis of congestive heart failure (NYHA Class I and II) was made on clinical grounds. Patients who were classified as having NYHA Class I congestive heart failure had received a diagnosis of the disease but had no symptoms. -
ATHENA study design3
- Double-blind, randomized, multicenter, placebo-controlled study to evaluate efficacy and safety of MULTAQ in 4628 patients ≥70 years of age with paroxysmal or persistent AFib/AFL and an additional CV risk factor
- Patients who experienced AFib/AFL within 6 months, and were in sinus rhythm, were randomized 1:1 to receive 400 mg MULTAQ twice daily or placebo
- Primary efficacy endpoint: First hospitalization due to CV event or death from any cause
Common CV comorbidities in patients in the ATHENA trial
AFib PATIENTS WITH DEFINED ADDITIONAL RISK FACTORS
(N=4628)2,386% Hypertension
60% Structural heart disease
30% Coronary artery disease
29% History of CHF (NYHA Class I to III)MULTAQ is contraindicated in patients with NYHA Class IV heart failure, symptomatic heart failure with recent decompensation requiring hospitalization, or permanent AFib.2
Common cardiovascular therapies treating patients in the MULTAQ and placebo arms1,3
AFib PATIENTS WITH DEFINED ADDITIONAL RISK FACTORS
(N=4628)2,371% Beta-blocker
69% ACE inhibitor or ARB
60% Oral anticoagulant
39% Statin
14% Calcium antagonistATHENA included 196 patients (4.2%) who had undergone ablation for AFib/AFL prior to randomization.4
Baseline characteristics3,*

*There were no significant differences between the 2 groups for any of the baseline characteristics, with the exception of the proportion of study patients who were women, which was significantly greater in the MULTAQ group (P=0.002).
†Complete data on structural heart disease were available for 2281 of the 2301 patients receiving MULTAQ, and for 2304 of the 2327 patients receiving placebo, for a total of 4585 patients.
‡For left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), data were available for 2263 of the 2301 patients receiving MULTAQ, and for 2281 of the 2327 patients receiving placebo, for a total of 4544 patients. The category of LVEF less than 45% included the patients with LVEF of less than 35%.
§Lone atrial fibrillation was defined as atrial fibrillation in the absence of cardiovascular disease and extracardiac precipitating causes of atrial fibrillation.
MULTAQ IS PROVEN TO REDUCE THE RISK OF AFIB RECURRENCE2
AAD=antiarrhythmic drug
ADONIS=American–Australian–African Trial With Dronedarone in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation or Atrial Flutter Patients for the Maintenance of Sinus Rhythm
AE=adverse event
AFib=atrial fibrillation
AFL=atrial flutter
ATHENA=A Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Parallel Arm Trial to Assess the Efficacy of Dronedarone 400 mg bid for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Hospitalization or Death From Any Cause in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation/Atrial Flutter
CAD=coronary artery disease
CI=confidence interval
CV=cardiovascular
ECG=electrocardiogram
EURIDIS=European Trial in Atrial Fibrillation or Flutter Patients Receiving Dronedarone for the Maintenance of Sinus Rhythm
HFpEF=heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
HR=hazard ratio
NNT=number needed to treat
RRR=relative risk reduction
TEAE=treatment-emergent adverse event
References
- Singh BN, Connolly SJ, Crijns HJ, et al. Dronedarone for maintenance of sinus rhythm in atrial fibrillation or flutter. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(10):987-999.
- MULTAQ [package insert]. Bridgewater, NJ. sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC; 2023.
- Hohnloser SH, Crijns HJ, van Eickels M, et al. Effect of dronedarone on cardiovascular events in atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(7):668-678.
- Thind M, Crijns HJ, Naccarelli GV, et al. Dronedarone treatment following cardioversion in patients with atrial fibrillation/flutter: a post hoc analysis of the EURIDIS and ADONIS trials. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2020;31(5):1022-1030.
Indication
MULTAQ is an antiarrhythmic drug indicated to reduce the risk of hospitalization for atrial fibrillation (AFib) in patients in sinus rhythm with a history of paroxysmal or persistent AFib.
Important Safety Information
Important Safety Information
WARNING: INCREASED RISK OF DEATH, STROKE AND HEART FAILURE IN PATIENTS WITH DECOMPENSATED HEART FAILURE OR PERMANENT ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
MULTAQ is contraindicated in patients with symptomatic heart failure with recent decompensation requiring hospitalization or NYHA Class IV heart failure. MULTAQ doubles the risk of death in these patients.
MULTAQ is contraindicated in patients in atrial fibrillation (AFib) who will not or cannot be cardioverted into normal sinus rhythm. In patients with permanent AFib, MULTAQ doubles the risk of death, stroke, and hospitalization for heart failure.
MULTAQ is also contraindicated in patients with:
- Second- or third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block or sick sinus syndrome (except when used in conjunction with a functioning pacemaker), bradycardia <50 bpm, QTc interval >500 ms or PR interval >280 ms
- Concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors, such as ketoconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole, cyclosporine, telithromycin, clarithromycin, nefazodone, ritonavir, erythromycin, or drugs or herbal products that prolong the QT interval and might increase the risk of torsade de pointes, such as phenothiazine antipsychotics, tricyclic antidepressants, certain oral macrolide antibiotics, and Class I and III antiarrhythmics
- Liver or lung toxicity related to the previous use of amiodarone
- Severe hepatic impairment
- Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients
Cardiovascular Death in NYHA Class IV or Decompensated Heart Failure
MULTAQ is contraindicated in patients with NYHA Class IV heart failure or symptomatic heart failure with recent decompensation requiring hospitalization because it doubles the risk of death.
Cardiovascular Death and Heart Failure in Permanent AFib
MULTAQ doubles the risk of cardiovascular death (largely arrhythmic) and heart failure events in patients with permanent AFib. Patients treated with dronedarone should undergo monitoring of cardiac rhythm no less often than every 3 months. Cardiovert patients who are in AFib (if clinically indicated) or discontinue MULTAQ. MULTAQ offers no benefit in subjects in permanent AFib.
Increased Risk of Stroke in Permanent AFib
In a placebo-controlled study in patients with permanent AFib, dronedarone was associated with an increased risk of stroke, particularly in the first 2 weeks of therapy. MULTAQ should only be initiated in patients in sinus rhythm who are receiving appropriate antithrombotic therapy.
New Onset or Worsening Heart Failure
New onset or worsening of heart failure has been reported during treatment with MULTAQ in the postmarketing setting. In a placebo-controlled study in patients with permanent AFib, increased rates of heart failure were observed in patients with normal left ventricular function and no history of symptomatic heart failure, as well as those with a history of heart failure or left ventricular dysfunction.
Advise patients to consult a physician if they develop signs or symptoms of heart failure, such as weight gain, dependent edema, or increasing shortness of breath. If heart failure develops or worsens and requires hospitalization, discontinue MULTAQ.
Liver Injury
Hepatocellular liver injury, including acute liver failure requiring transplant, has been reported in patients treated with MULTAQ in the postmarketing setting. Advise patients treated with MULTAQ to report immediately symptoms suggesting hepatic injury (such as anorexia, nausea, vomiting, fever, malaise, fatigue, right upper quadrant pain, jaundice, dark urine, or itching). Consider obtaining periodic hepatic serum enzymes, especially during the first 6 months of treatment. It is not known whether routine periodic monitoring of serum enzymes will prevent the development of severe liver injury. If hepatic injury is suspected, promptly discontinue MULTAQ and test serum enzymes, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and alkaline phosphatase, as well as serum bilirubin, to establish whether there is liver injury. If liver injury is found, institute appropriate treatment and investigate the probable cause. Do not restart MULTAQ in patients without another explanation for the observed liver injury.
Pulmonary Toxicity
Cases of interstitial lung disease including, pneumonitis and pulmonary fibrosis, have been reported in patients treated with MULTAQ in the post-marketing setting. Onset of dyspnea or non-productive cough may be related to pulmonary toxicity and patients should be carefully evaluated clinically. If pulmonary toxicity is confirmed, MULTAQ should be discontinued.
Hypokalemia and Hypomagnesemia with Potassium-Depleting Diuretics
Hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia may occur with concomitant administration of potassium-depleting diuretics. Potassium levels should be within the normal range prior to administration of MULTAQ and maintained in the normal range during administration of MULTAQ.
QT Interval Prolongation
MULTAQ is associated with concentration-dependent QTcF interval prolongation (estimated QTcF increase for 400 mg BID with food is 15 ms). If the QTc interval is >500 ms, discontinue MULTAQ.
Renal Impairment and Failure
Marked increase in serum creatinine, pre-renal azotemia and acute renal failure, often in the setting of heart failure or hypovolemia, have been reported in patients taking MULTAQ. In most cases, these effects appear to be reversible upon drug discontinuation and with appropriate medical treatment. Monitor renal function periodically.
Small increases in creatinine levels (about 0.1 mg/dL) following MULTAQ treatment initiation have been shown to be a result of inhibition of creatinine’s tubular secretion. The elevation has a rapid onset, reaches a plateau after 7 days and is reversible after discontinuation.
Embryofetal Toxicity
Based on animal data, MULTAQ may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Dronedarone caused multiple visceral and skeletal malformations in animal reproduction studies when pregnant rats and rabbits were administered dronedarone at doses equivalent to recommended human doses. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to the fetus. Verify that females of reproductive potential are not pregnant prior to initiating MULTAQ. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with MULTAQ and for 5 days (about 6 half-lives) after the final dose.
Drug-Drug Interactions
- Treatment with Class I or III antiarrhythmics or drugs that are strong inhibitors of CYP3A must be stopped before starting MULTAQ (see Contraindications)
- Patients should be instructed to avoid grapefruit juice beverages while taking MULTAQ
- Calcium channel blockers with depressant effects and beta-blockers could increase the bradycardia effects of MULTAQ on conduction
- In the ANDROMEDA (patients with recently decompensated heart failure) and PALLAS (patients with permanent AFib) trials, baseline use of digoxin was associated with an increased risk of arrhythmic or sudden death in dronedarone-treated patients compared to placebo. In patients not taking digoxin, no difference in risk of sudden death was observed in the dronedarone vs. placebo groups.
- Digoxin can potentiate the electrophysiologic effects of dronedarone (such as decreased AV-node conduction). dronedarone increases exposure to digoxin.
- Consider discontinuing digoxin. If digoxin treatment is continued, halve the dose of digoxin, monitor serum levels closely, and observe for toxicity.
- Postmarketing cases of increased INR with or without bleeding events have been reported in warfarin-treated patients initiated with dronedarone. Monitor INR after initiating MULTAQ in patients taking warfarin
- Statins: Avoid simvastatin doses greater than 10 mg daily. Follow statin label recommendations for use with CYP3A and P-gp inhibitors such as dronedarone
Adverse Reactions
In studies, the most common adverse reactions (≥2%) observed with MULTAQ were diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, dyspepsia, bradycardia, skin issues (rashes, pruritus, eczema, dermatitis, dermatitis allergic), and asthenia.
Use in Specific Populations
Lactation: Do not breastfeed
Please click here for full Prescribing Information including Boxed WARNING.
Click here to learn more about Sanofi's commitment to fighting counterfeit drugs.
Important Safety Information
WARNING: INCREASED RISK OF DEATH, STROKE AND HEART FAILURE IN PATIENTS WITH DECOMPENSATED HEART FAILURE OR PERMANENT ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
MULTAQ is contraindicated in patients with symptomatic heart failure with recent decompensation requiring hospitalization or NYHA Class IV heart failure. MULTAQ doubles the risk of death in these patients.
MULTAQ is contraindicated in patients in atrial fibrillation (AFib) who will not or cannot be cardioverted into normal sinus rhythm. In patients with permanent AFib, MULTAQ doubles the risk of death, stroke, and hospitalization for heart failure.
MULTAQ is also contraindicated in patients with:
- Second- or third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block or sick sinus syndrome (except when used in conjunction with a functioning pacemaker), bradycardia <50 bpm, QTc interval >500 ms or PR interval >280 ms
- Concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors, such as ketoconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole, cyclosporine, telithromycin, clarithromycin, nefazodone, ritonavir, erythromycin, or drugs or herbal products that prolong the QT interval and might increase the risk of torsade de pointes, such as phenothiazine antipsychotics, tricyclic antidepressants, certain oral macrolide antibiotics, and Class I and III antiarrhythmics
- Liver or lung toxicity related to the previous use of amiodarone
- Severe hepatic impairment
- Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients
Cardiovascular Death in NYHA Class IV or Decompensated Heart Failure
MULTAQ is contraindicated in patients with NYHA Class IV heart failure or symptomatic heart failure with recent decompensation requiring hospitalization because it doubles the risk of death.
Cardiovascular Death and Heart Failure in Permanent AFib
MULTAQ doubles the risk of cardiovascular death (largely arrhythmic) and heart failure events in patients with permanent AFib. Patients treated with dronedarone should undergo monitoring of cardiac rhythm no less often than every 3 months. Cardiovert patients who are in AFib (if clinically indicated) or discontinue MULTAQ. MULTAQ offers no benefit in subjects in permanent AFib.
Increased Risk of Stroke in Permanent AFib
In a placebo-controlled study in patients with permanent AFib, dronedarone was associated with an increased risk of stroke, particularly in the first 2 weeks of therapy. MULTAQ should only be initiated in patients in sinus rhythm who are receiving appropriate antithrombotic therapy.
New Onset or Worsening Heart Failure
New onset or worsening of heart failure has been reported during treatment with MULTAQ in the postmarketing setting. In a placebo-controlled study in patients with permanent AFib, increased rates of heart failure were observed in patients with normal left ventricular function and no history of symptomatic heart failure, as well as those with a history of heart failure or left ventricular dysfunction.
Advise patients to consult a physician if they develop signs or symptoms of heart failure, such as weight gain, dependent edema, or increasing shortness of breath. If heart failure develops or worsens and requires hospitalization, discontinue MULTAQ.
Liver Injury
Hepatocellular liver injury, including acute liver failure requiring transplant, has been reported in patients treated with MULTAQ in the postmarketing setting. Advise patients treated with MULTAQ to report immediately symptoms suggesting hepatic injury (such as anorexia, nausea, vomiting, fever, malaise, fatigue, right upper quadrant pain, jaundice, dark urine, or itching). Consider obtaining periodic hepatic serum enzymes, especially during the first 6 months of treatment. It is not known whether routine periodic monitoring of serum enzymes will prevent the development of severe liver injury. If hepatic injury is suspected, promptly discontinue MULTAQ and test serum enzymes, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and alkaline phosphatase, as well as serum bilirubin, to establish whether there is liver injury. If liver injury is found, institute appropriate treatment and investigate the probable cause. Do not restart MULTAQ in patients without another explanation for the observed liver injury.
Pulmonary Toxicity
Cases of interstitial lung disease including, pneumonitis and pulmonary fibrosis, have been reported in patients treated with MULTAQ in the post-marketing setting. Onset of dyspnea or non-productive cough may be related to pulmonary toxicity and patients should be carefully evaluated clinically. If pulmonary toxicity is confirmed, MULTAQ should be discontinued.
Hypokalemia and Hypomagnesemia with Potassium-Depleting Diuretics
Hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia may occur with concomitant administration of potassium-depleting diuretics. Potassium levels should be within the normal range prior to administration of MULTAQ and maintained in the normal range during administration of MULTAQ.
QT Interval Prolongation
MULTAQ is associated with concentration-dependent QTcF interval prolongation (estimated QTcF increase for 400 mg BID with food is 15 ms). If the QTc interval is >500 ms, discontinue MULTAQ.
Renal Impairment and Failure
Marked increase in serum creatinine, pre-renal azotemia and acute renal failure, often in the setting of heart failure or hypovolemia, have been reported in patients taking MULTAQ. In most cases, these effects appear to be reversible upon drug discontinuation and with appropriate medical treatment. Monitor renal function periodically.
Small increases in creatinine levels (about 0.1 mg/dL) following MULTAQ treatment initiation have been shown to be a result of inhibition of creatinine’s tubular secretion. The elevation has a rapid onset, reaches a plateau after 7 days and is reversible after discontinuation.
Embryofetal Toxicity
Based on animal data, MULTAQ may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Dronedarone caused multiple visceral and skeletal malformations in animal reproduction studies when pregnant rats and rabbits were administered dronedarone at doses equivalent to recommended human doses. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to the fetus. Verify that females of reproductive potential are not pregnant prior to initiating MULTAQ. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with MULTAQ and for 5 days (about 6 half-lives) after the final dose.
Drug-Drug Interactions
- Treatment with Class I or III antiarrhythmics or drugs that are strong inhibitors of CYP3A must be stopped before starting MULTAQ (see Contraindications)
- Patients should be instructed to avoid grapefruit juice beverages while taking MULTAQ
- Calcium channel blockers with depressant effects and beta-blockers could increase the bradycardia effects of MULTAQ on conduction
- In the ANDROMEDA (patients with recently decompensated heart failure) and PALLAS (patients with permanent AFib) trials, baseline use of digoxin was associated with an increased risk of arrhythmic or sudden death in dronedarone-treated patients compared to placebo. In patients not taking digoxin, no difference in risk of sudden death was observed in the dronedarone vs. placebo groups.
- Digoxin can potentiate the electrophysiologic effects of dronedarone (such as decreased AV-node conduction). dronedarone increases exposure to digoxin.
- Consider discontinuing digoxin. If digoxin treatment is continued, halve the dose of digoxin, monitor serum levels closely, and observe for toxicity.
- Postmarketing cases of increased INR with or without bleeding events have been reported in warfarin-treated patients initiated with dronedarone. Monitor INR after initiating MULTAQ in patients taking warfarin
- Statins: Avoid simvastatin doses greater than 10 mg daily. Follow statin label recommendations for use with CYP3A and P-gp inhibitors such as dronedarone
Adverse Reactions
In studies, the most common adverse reactions (≥2%) observed with MULTAQ were diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, dyspepsia, bradycardia, skin issues (rashes, pruritus, eczema, dermatitis, dermatitis allergic), and asthenia.
Use in Specific Populations
Lactation: Do not breastfeed
Please click here for full Prescribing Information including Boxed WARNING.
Click here to learn more about Sanofi's commitment to fighting counterfeit drugs.